PSA - Prostate cancer alarm
The previous part said that the incidence and mortality of prostate cancer in China remain high, and early diagnosis and early detection can be early treatment, improve the quality of life and prolong life. With the improvement and development of prostate cancer diagnosis technology in our country, researchers have made great progress in basic and clinical research, especially the diagnosis rate has increased significantly. Of course, this progress cannot be achieved without tumor markers. What are tumor markers? Tumor markers (TM) are substances synthesized, released by tumor cells themselves, or produced or elevated by the body in response to tumor cells. Tumor markers exist in blood, cells, tissues or body fluids, reflecting the existence and growth of tumors. The determination of tumor markers by chemical, immunological and genomic methods is of certain value for the diagnosis, efficacy, recurrence monitoring and prognosis of tumors.
Prostate-specific antigen
Psa-related index Part.1 tPSA Serum total PSA, normal value 0 ~ 4ng/ml. Part.2 f/tPSA The percentage of free prostate-specific antigen, normal value > 0.16, when tPSA in the 4 ~ 10ng/ml gray zone, f/tPSA < 0.16 can improve the detection rate of prostate cancer. Part.3 PSAD Prostate-specific antigen density, that is, the ratio of total serum PSA value to prostate volume, normal value is PSAD < 0.15ng/(ml·/cm3). When tPSA is in the gray zone of 4 to 10ng/ml, PSAD can guide whether to biopsy or follow-up. Part.4 PSAV Prostate-specific antigen rate, that is, continuous observation of serum PSA changes, PSA detection at least 3 times in 2 years, PSAV=[(PSA2-PSA1)+(PSA3-PSA2)]/2, the normal value is < 0.75ng/(ml· year). If PSAV > 0.75 ng/(ml· year), the possibility of prostate cancer should be suspected. Part.5 PHI Prostate Health Index, PHI=(p2PSA/fPSA) *√PSA. Studies based on the Chinese population showed that when PHI tangent point values were < 27, 27 ~ 36, 36 ~ 55 and ≥55, the probability of prostate cancer was 9.8%, 16.8%, 33.3% and 50.1%, respectively. Part.6 PSADT Prostate-specific antigen doubling time refers to the time required for PSA levels to double. PSADT is a risk predictor of developing prostate cancer metastasis, and faster PSADT is associated with a shorter time to metastasis.
Clinical significance
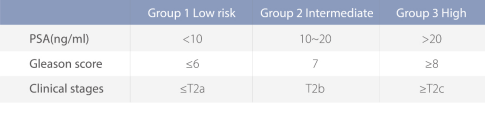
PSA screening recommendations Prostate cancer screening is a systematic examination of asymptomatic men with PSA detection as the main means, the main purpose of which is to reduce the mortality rate of prostate cancer in the screening population and not affect the quality of life of the screening population. The significance of prostate cancer screening is to improve the detection rate of prostate cancer and find early prostate cancer, especially the prostate cancer with clinical significance. Prostate cancer screening targets: Psa-based prostate cancer screening for men in good health with a life expectancy of more than 10 years; The PSA test should be tested every 2 years, and the termination time of PSA test should be determined according to the age and physical condition of the patient. ③ The prostate cancer high-risk group should pay attention to screening. High-risk groups include: men >50 years old; Men >45 years old with a family history of prostate cancer; Men >40 years of age with baseline PSA>1ng/mL.
At present, a basic consensus has been reached in clinical practice to determine the progression of prostate cancer by detecting PSA and to diagnose prostate cancer by detecting f/tPSA. We will cherish valuable resources, rely on scientific research methods, carry out beneficial exploration and summary, put forward convincing data, so that prostate cancer patients get early, reasonable, ideal diagnosis and treatment. reference [1] Qin Haiqiu. Research on PSA in the diagnosis of prostate cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Diagnostics,2012,16(6):1105-1106. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2012.06.059. (in Chinese) [2].Ogino S,Kawaguchi M,Okuizumi M, et al. Application of serum PSA to identify acute bacterial prostatitis in patients with fever of unknown origin or symptoms of acute pyelonephritis.[J].The Prostate.2004,60(4). [3].NCCN guidelines version 2.2022 prostate cancer. [4].Consensus statement: guidlines for PSA following radiation therapy. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology Consensus [5].Panel. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1997; 37:1035-41. [6].Rebecka Arnsrud Godtman,Long-term Results of Active Surveillance in the Go¨teborg Randomized, Population-based Prostate Cancer Screening Trial, EURURO-6759; No. of Pages 7. [7].American Urological Association (AUA).