In vitro diagnostic technology based on liquid biopsy
In the previous two articles, we discussed that the three chariots of liquid biopsy are CTCS, ctDNA and exosomes, through which biomarkers can diagnose and monitor tumors and other diseases. Compared with tissue biopsy, liquid biopsy has the advantages of non-interventional, repeatable acquisition of tumor samples, low side effects, simple operation, low cost, fast detection speed and wide indications. While reducing the deviation caused by tumor heterogeneity in diagnosis, liquid biopsy can also timely reflect the dynamic changes of tumor development.
In vitro diagnosis based on liquid biopsy can be divided into biochemical diagnosis, immunodiagnosis and molecular diagnosis according to methodology, as well as POCT, a rapid bedside diagnosis differentiated from biochemical, immunodiagnosis and molecular diagnosis. This article will provide an overview of these in vitro diagnostic techniques
In vitro diagnosis based on liquid biopsy can be divided into biochemical diagnosis, immunodiagnosis and molecular diagnosis according to methodology, as well as POCT, a rapid bedside diagnosis differentiated from biochemical, immunodiagnosis and molecular diagnosis. This article will provide an overview of these in vitro diagnostic techniques.
Biochemical diagnosis
Biochemistry Diagnostic
Biochemical diagnosis refers to the diagnostic method involving enzyme reaction or antigen and antibody reaction, which is mainly used for the determination of biochemical indicators such as enzymes, sugars, lipids, protein and non-protein nitrogen, inorganic elements and other biological function indicators or proteins. It is one of the most commonly used diagnostic methods in vitro at present.
Biochemical diagnosis developed early in China. It is a routine diagnostic testing project in hospitals, focusing on disease monitoring that has already occurred. In the future, the growth rate will be slow, and the reagent localization rate has reached more than 70%. Most of the instruments have also been made in China. At present, the domestic instruments only have a gap with foreign instruments in the speed and integration of instrument testing.
immunodiagnosis
Immunodiagnostics
Immunodiagnosis is the application of immunological theories, techniques and methods to diagnose various diseases and determine immune status, which can be carried out in vivo and in vitro. In medicine, it is an important method to determine the cause of disease and lesion site or to determine whether the immune state of the body is normal. In forensic medicine, it is used for the identification of blood stains, the identification of serum components in biochemistry and the study of the evolutionary relationship of species. For example, ctDNA carries comprehensive genomic variation information of tumor cells, which can not only evaluate the relationship between the mutation of a single gene and the efficacy of immunotherapy, but also the total number of ctDNA mutations can be used as predictive markers of immunotherapy[1]. In addition, some studies have reported that immune cells and immune factors can also predict the efficacy of immune drugs[2-3].
Immunodiagnostics is the largest subdivided in vitro diagnostic subindustry in China and is still in rapid development. High-end chemiluminescence has gradually replaced enzyme linked immunization as the mainstream immunodiagnostic method in China, focusing on the surveillance of already infected diseases, and the market size has reached more than 70% of the total immunodiagnostics market. Medium and low-end reagents and instruments are highly localized, but the high-end market such as tertiary hospitals is still monopolized by overseas giants. In the future, import substitution is the development direction of high-end immunodiagnostic market.
Molecular diagnosis
Molecular Diagnostic
Molecular diagnosis, which relies on molecular biology technology, has become a frontier of clinical medicine, and plays an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases, tumors and other diseases. Molecular diagnosis mainly detects nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, using the principle of nucleic acid hybridization, primers and probes are commonly used tools. Current technologies and methods based on clinical detection include mutation/mutation detection technology, DNA sequencing technology, biochip technology, PCR technology, fluorescence in situ hybridization technology FISH, capillary electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Molecular diagnostics are in the early stage of development worldwide and have unique advantages in detecting the early stage of infection and possible genetic diseases.
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR is to add fluorescein labeled probe (such as fluorescein labeled Taqman probe) or corresponding fluorescent dye on the basis of conventional PCR to achieve quantitative purposes. At present, the practical diseases include hereditary diseases, infectious diseases and tumors. The abnormal expression of ZXF1 in lung gland tissue is closely related to the degree of tumor differentiation and lymph node metastasis. In clinical practice, its high expression can predict the poor prognosis of patients, and conclude that ZXF1 may affect the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by enhancing the expression of target proteins BMP-5 and SCFR. The clinical application of qRT-PCR can detect the expression level of ZXF1 mRNA sensitively and accurately [4].

Figure 1 Principle of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technology (Source: Soler M,et al,APL Photonics, 2020[5])
Nucleic acid hybridization
Nucleic acid hybridization is a common method in genetic research and gene diagnosis. It mainly includes reverse spot hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular biological technique to detect chromosome, gene number and structure abnormalities at the cytogenetic level. researcher[6]It was found that the genetic changes of chromosome 9 (p16), chromosome 3, chromosome 7 and chromosome 17 were closely related to the early occurrence, development and recurrence of bladder cancer. Therefore, it is of great significance to use this non-invasive, highly sensitive and highly specific FISH technique to detect aberrant chromosomes in urine samples for early diagnosis and postoperative monitoring of bladder cancer.
Reverse dot hybridization has the advantages of simultaneous detection and screening of multiple samples, short preparation time of film strips, non-radioactive labeling primers and avoiding stability problems caused by isotope half-life.
DNA sequencing test
Continuous iteration and update of sequencing technology make sequencing results more rapid and accurate. Sanger method, as the first generation sequencing technology, is also known as dideoxyribonucleic acid terminal termination method. The sequencing steps include template separation, cyclic sequencing, purification of sequencing products, capillary electrophoresis, data analysis, etc.
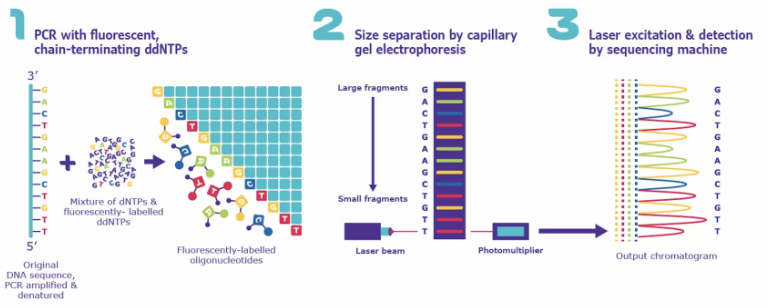
Figure 2 Principle of Sanger Method (Source: Network)
Although Sanger sequencing method has high accuracy, the length of one sequencing is only 300-1000bp, with low flux and slow speed, leading to the emergence of the second generation sequencing technology, which adopts microcycle array synthesis sequencing method. High-throughput sequencing, also known as next-generation sequencing technology, can simultaneously sequence hundreds of thousands to millions of DNA molecules in parallel. Some scholars used NGS detection to find the methylation of 12 gene promoators (ARHGAP6, HAND2, LHX9, HEY2, NKX2-2, PCDH10, PITX2, PROX1, TBX3, IKBKG, RAB6CHE, DAPK1) in cervical cancer cell lines. This provides an effective marker of gene-specific methylation for the early detection and clinical management of cervical cancer [7].
At present, second-generation sequencing is also the most widely used sequencing technology. With the continuous development of technology, third-generation single-molecule sequencing and fourth-generation nanopore sequencing are also gradually emerging.
Table 1 Comparison of three diagnostic techniques
method | Representative technique | advantage | shortcomings | Application field |
Biochemical diagnosis | Latex enhanced immune turbidimetric technology | High demand, low cost, fast detection speed, one of the leading domestic varieties | Long time, cumbersome operation, radioactive pollution | Liver function, kidney function, diabetes, blood lipid, cardiovascular, rheumatism, etc |
Enzyme cycle technique | Limited detection range | |||
immunodiagnosis | Colloidal gold | Fast, simple, accurate and pollution-free | The detection sensitivity is not high and the detection range is limited | Virus and blood detection, hepatitis detection, STD detection, tumor detection, etc |
Enzyme-linked immunity | Low cost, fast | Detection sensitivity is not high, reagent preservation time is short, need manual operation | ||
chemiluminescence | Wide linear range, high sensitivity, strong specificity, high automation, fast detection speed, not affected by the number of samples, reagent quality is stable | Low detection flux | ||
Molecular diagnosis | PCR | Strong specificity, high sensitivity, simple and fast | Low detection flux | Infectious diseases (influenza, hepatitis, venereal diseases, etc.), genetic diseases, tumors, etc |
In situ hybridization | Lower cost | The accuracy is relatively low and the detection flux is small | ||
Gene chip | Detection, convenient, accurate | Low detection flux | ||
Gene sequencing | Large amount of information, high flux and accuracy | High cost and long time |
Point-of-care detection (POCT)
POCT refers to the method of instant analysis at the sampling site and quick results obtained by using portable analytical instruments and supporting reagents. Compared with other in vitro diagnostic tests, POCT has the greatest feature of immediateness, immediateness and simplicity. It is less than one minute at the earliest, and can be operated by anyone on the spot regardless of conditions.
POCT is usually accomplished through the use of portable, portable, and handheld instruments (e.g., blood glucose meters, nerve conduction research equipment) and test kits (e.g., CRP, HBA1C, homocysteine, HIV saliva assay, etc.). When handheld devices are not available, small desktop analyzers or stationary devices can also be used - the aim is to collect specimens at or near the patient's location and obtain results in a very short time so that treatment plans can be adjusted as needed before the patient leaves[8] .

Figure 3 Real-time detection technology (Source: Leila Syedmoradi, et al,Talanta,2021[9])
Cheaper, faster, and smarter POCT devices have increased the use of the POCT method, making it cost-effective for many diseases, such as diabetes, carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)[10]And acute coronary syndrome. In addition, the simultaneous measurement of multiple analytes in the same sample, so as to achieve rapid, low-cost and reliable quantization has become a new trend[11]. As a result, multiple point-of-care tests (xPOCT) have become increasingly important for medical diagnosis over the past decade[12].
For years, researchers have understood the clinical potential of liquid biopsies. More interventional clinical trials and the development of an algorithm to incorporate suitable circulating biomarkers are needed to advance their widespread use. With the continuous progress of detection technology, it is believed that liquid biopsy will become a new trend of precision medicine in the future.
Reference literature
[1] Khagi Y, Goodman A M, Daniels G A, et al. Hypermutated circulating tumor dna:correlation with response to checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res,2017,23:5729-5736.
[2] Krieg C, Nowicka M, Guglietta S,et al. High-dimensional single-cell analysis predicts response to anti-PD-1immunotherapy.Nature Journal of Medicine,2018,24 (2) :144-153.
[3] Sanmamed M, Perez-Gracia J,Schalper K, et al. Changes in serum interleukin-8(IL-8) levels reflect and predict response to anti-PD-1 treatment inmelanoma and non-small cell lung cancer patients.Annals of Oncology, 2017,28(8):1988-1995.
[4] Pan GF,Zhou XF,Zhao JP.Correlation between expression of long non-coding RNA ZXF1 and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma and its potential molecular mechanism[J].Zhonghua ZhongLiu Za Zhi,2017,39(2):102-108.
[5] Soler M, Scholtz A, Zeto R, et al. Engineering photonics solutions for COVID-19. APL Photonics. 20,5(9).
[6] Phillips JL,Richardson IC.Aneuploidy in bladder cancers:the u-tility of fluorescent in situ hybridization in BJU Int,2006,98(1):33-37.
[7] Bhat S, Kabekkodu SP, Varghese VK,et al.Aberrant gene-specific DNA methylation signature analysis in cervical cancer[J].Tumor Biol, 2017, 33 (3) 6:101042831769457.
[8] College of American Pathologists POCT toolkit". Archived from the original on 2010-12-22.
[9] Leila Syedmoradi, Michael L. Norton, Kobra Omidfar, Point-of-care cancer diagnostic devices: From academic research to clinical translation, Talanta, Volume 225, 2021, 122002.
[10] Tolonen U, Kallio M, Ryhänen J, Raatikainen T, Honkala V, Lesonen V (June 2007). "A handheld nerve conduction measuring device in carpal tunnel syndrome". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 115 (6): 390-7.
[11] Spindel S, Sapsford KE (November 2014). "Evaluation of optical detection platforms for multiplexed detection of proteins and the need for point-of-care biosensors for clinical use". Sensors. 14 (12): 22313-41.
[12] Dincer C, Bruch R, Kling A, Dittrich PS, Urban GA (August 2017). "Multiplexed Point-of-Care Testing - xPOCT". Trends in Biotechnology. 35 (8): 728-742.

