Sample pretreatment ---- means to reduce error in analysis
Rationale
Sample pretreatment refers to a series of preparatory work before the analysis and determination, separating the substance to be measured from the sample matrix or interference substances in the sample, so that it can be analyzed by the instrument.
Ocular
Many complex samples exist in a heterogeneous form, such as oil aerosols and floating dust in the atmosphere, emulsions, solid particles and suspended matter contained in wastewater, water in the soil, microorganisms, stones, etc., so complex samples must be analyzed after pre-treatment. Both clinical biological samples and ordinary healthy subjects contain a large number of endogenous macromolecules, which makes the analysis results susceptible to matrix effects. Therefore, the purpose of sample pre-processing is to:
1. Concentrate trace components to improve the sensitivity of the method and reduce the detection limit;
2. Remove the matrix and other interfering substances in the sample;
3. Through derivatization and other reactions, the measured object is converted into a substance with higher detection sensitivity or into a substance that can be separated from the interfering components in the sample, so as to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of the method;
4. Concentrate the quality and volume of the sample, facilitate transportation and preservation, improve the stability of the sample, so that it is not affected by air;
5. Protect analytical instruments and test systems, so as not to affect the performance and life of instruments;
General principles for handling biological samples
At present, the types of biological samples commonly used are blood samples (plasma, serum, whole blood), urine, tears, feces, etc. This kind of sample is easy to obtain, easy to process and analyze, and can also reflect the relationship between concentration and drug effect. In the analysis of biological samples, except in rare cases, the sample can be directly determined by simple treatment, and other pretreatment technologies such as separation, purification, concentration and chemical derivatization need to be adopted to create good conditions for the determination. For example, biological samples homogenize body fluid samples (urine, plasma, etc.) by vortex mixing; Solid samples (such as tissue, feces, etc.) need to add an appropriate amount of solvent for high-speed homogenization.
Technik
At present, the common treatment methods of biological samples include protein precipitation, liquid-liquid extraction and solid phase extraction.
Protein Precipitation (PPT)
① Rationale
Precipitation is the process in which the solute in the solution changes from the liquid phase to the solid phase. The precipitation of proteins from solution is called protein precipitation. Protein precipitation is an important step in the pretreatment of proteome. The influencing factors include solvent type, ionic strength, precipitation time, temperature and so on. Different precipitation conditions will bring different protein recovery and proteome coverage. Samples such as plasma, serum, and whole blood are rich in soluble proteins, and these protein components can not only interfere with the detection of analytes, causing serious matrix effects, but may also clog the column and instrument pipes and damage the instrument. Therefore, the protein in the sample needs to be removed.
② Advantages and disadvantages
The common method in clinical mass spectrometry field is to add organic solvent, reduce the dielectric constant of water, and dehydrate biological macromolecules with surface water layer, aggregate with each other, and finally precipitate. The resolution of this method is better than that of salting-out method, that is, the protein is only precipitated at a relatively narrow organic concentration. And there is no need to consider salt removal after precipitation, and it is easier to filter. However, the disadvantage is that only the protein is removed, and the endogenous impurities remain, and the long detection time may affect the life of the column and the instrument. Adding too much organic solvent will dilute the sample concentration after treatment, which will not only reduce the detection sensitivity, but also may lead to solvent effect.
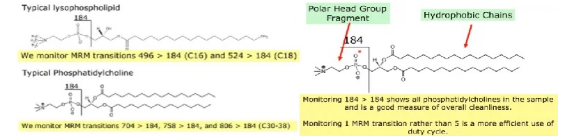
Figure 1 Monitoring phospholipid molecular MRM (Source network)
Liquid-liquid extraction (LLE)
① Rationale
Liquid-liquid extraction method is based on the similar compatibility principle of analyte, using the analyte and the interferant in two incompatible solvents partition coefficient is different, so that the analyte is separated from the interferant, so as to achieve the sample purification. When the samples were processed by liquid-liquid extraction, the analytes migrated from the water layer of the sample to the organic solvent layer. After centrifugation, the organic solvent layer was removed, and the sample was reconstructed with a solvent that was miscible with water after blowing dry with nitrogen. Therefore, liquid-liquid extraction method is suitable for sample pretreatment when analyzing compounds with low polarity.
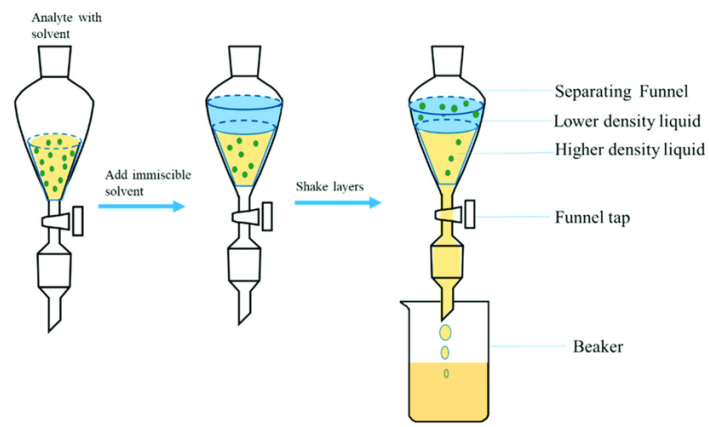
FIG. 2 Principle of liquid-liquid extraction (source network)
② Advantages and disadvantages
Due to the principle of two-phase migration used in liquid-liquid extraction, the analytes in plasma, serum or urine need to migrate from the water layer to the organic solvent layer, and protein molecules and hydrophilic small molecules are removed during this process. Therefore, the purification degree of liquid-liquid extraction method is higher than that of protein precipitation method, which is conducive to the improvement of analytical sensitivity. On the other hand, different from methanol and acetonitrile commonly used in protein precipitation method, solvents such as n-hexane, ethyl acetate or methyl tert-butyl ether added in liquid-liquid extraction method are extremely volatile, which is conducive to sample concentration, so the analytical sensitivity can be improved by concentrating samples when using liquid-liquid extraction method. Steroid hormones, fat-soluble vitamins and vitamin D were concentrated by liquid-liquid extraction.
The disadvantages of liquid-liquid extraction are: first, it is very limited by the polarity of the compound, the extraction efficiency of medium polarity compounds is very poor, and the recovery rate can not be satisfactory; Second, the liquid-liquid extraction method needs extraction, centrifugation, nitrogen blowing, reconstruction and other steps, the operation is more complicated, not conducive to automation; Third, the solvent used in liquid-liquid extraction is relatively volatile and not friendly to the environment.
Solid phase extraction (SPE)
① Rationale
Solid phase extraction (SPE) columns can be understood as special chromatographic columns, and the principle of column separation is roughly the same. After the sample is passed through the one-time extraction column filled with adsorbent, according to the different binding ability of the analyte and the interferant with the extraction column adsorbent, the impurities can be removed by different solvents of different polarity, and finally the analyte is eluted to achieve the purpose of separation and enrichment of the analyte. According to the different removal modes of interference, solid phase extraction can be divided into three kinds: filter plate (adsorption), retention of interference (through), retention of target (retention), of which the most commonly used is retention.
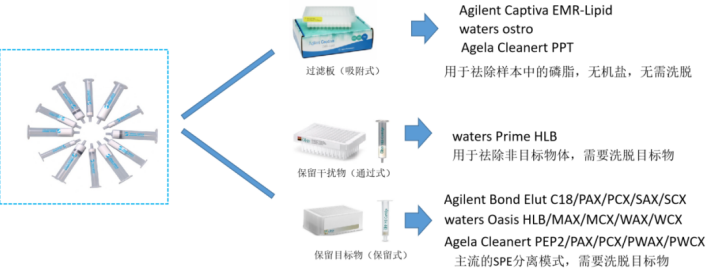
Figure 3 Classification of solid phase extraction (source network)
② Selection of solid phase extraction column
If there are more interference components in the sample and the analyte concentration is low, solid phase extraction can be used to treat the sample in order to remove the interference to the greatest extent and concentrate the sample volume. Solid phase extraction is the sample processing method with the highest degree of purification, which can effectively improve the sensitivity of analyte, and is also the processing method with the highest cost and the lowest flux.
Solid phase extraction columns with pure reversed phase fillers are generally suitable for the treatment of intermediate and weakly polar compounds. For example, when testing steroid hormones (testosterone, estradiol, estriol, aldosterone), the concentration level of some hormones is only pg grade, at this time, the samples can be treated with reversed phase solid phase extraction columns such as oasis HLB, Cleanert PEP, etc.
The ion exchange solid phase extraction column is used to purify the sample through the dual action of reverse phase and ion exchange. For example, when analyzing weakly acidic compounds such as sialic acid and methylmalonic acid, a mixed anion exchange solid phase extraction column (MAX or PAX) is selected to process the sample. The quaternary ammonium group in this kind of solid phase extraction column can be positively charged in the PH range of 1~14, firmly binding the carboxyl group of weakly acidic substances, and the interference components such as neutral and alkaline compounds without charge can be removed in the leaching step, and finally the charge of the analyte is inhibited by acidic eluent (carbinol formate or acetonitrile formate), and the analyte is eluted and collected. For example, when analyzing weak basic compounds such as clenbuterol and carnitine, a mixed cation exchange solid phase extraction column (MCX or PCX) is selected to process the sample. The sulfonic acid group in this kind of solid phase extraction column can be negatively charged in the PH range of 1~14, firmly binding the amine group of weak alkaline substances, non-charged neutral compounds, acidic compounds and other interfering components can be removed in the leaching step, and finally with alkaline eluent (ammonia methanol or ammonia acetonitrile) to inhibit the charge of the analyte, the analyte is eluted and collected.
In addition to the above two ion-exchange solid phase extraction columns, there are weak cation and weak anion exchange solid phase extraction columns (such as WCX and WAX). The packing in the weak cation exchange column contains carboxyl group, which is not charged in low PH environment and is negatively charged in high PH environment (such as PH>10). For example, in the analysis of catecholamine compounds, the carboxyl group in the WCX column is combined with the amine functional group of catecholamine in an alkaline environment. At this time, the neutral and acidic interferences in the sample can be removed with an alkaline eluent, and finally, the ion exchange force can be removed with ammonia and methanol by inhibiting the ionization of the carboxyl group in the fillers, so that the analytes are eluted and collected.
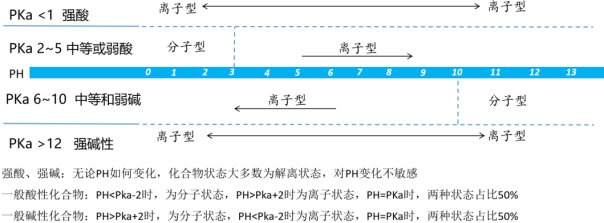
FIG. 4 Compound states at different PH (source network)
The traditional solid phase extraction column is not easy to control the flow rate of droplets because of the use of negative pressure device to provide the power of washing and elution, which is not only cumbersome in operation, but also poor in sample processing precision. At present, when solid phase extraction is used to process samples in clinical mass spectrometry testing projects, most of them use 96-hole solid phase extraction plate or solid phase extraction packing bonded to the surface of magnetic beads, and use positive pressure to control the flow rate of droplets, which greatly improves the parallelism of operation and is conducive to the automatic process of sample processing.
Although the above sample pretreatment methods developed in recent years have their own characteristics, they also have drawbacks. As an important part of the analysis results, sample pretreatment determines the success or failure of the experiment. This article hopes to let you understand the importance of sample pretreatment, and also hope that this article will be helpful to you.

